bigdata 연구실 선행학습으로 c언어를 이용하여 single linked list를 구현해보았다.
linked list는 아래의 그림과 같이 데이터가 저장되어있는 단위메모리가 연결형태를 나타낸다.
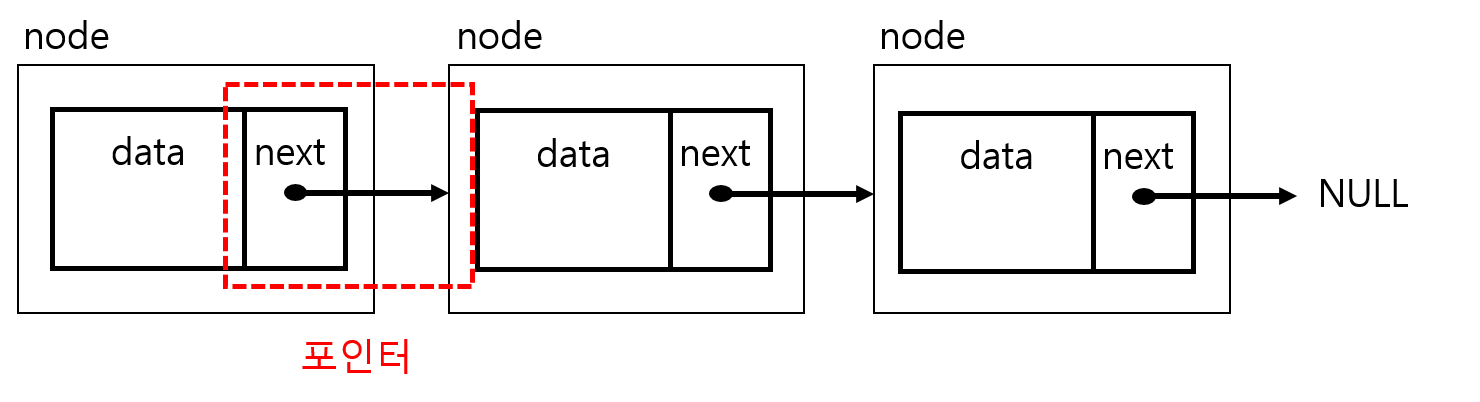
이 때 메모리를 연결하기 위해서 포인터를 사용하며 다음(next)을 나타내는 포인터가 다음 노드를 가리키게 되면서 메모리들을 연결하여 준다.
linked list 장점 -linked list는 삽입이 자유로워 생성 때 부터 메모리의 크기를 정하여 할당해주는 Array List와는 달리 추가적으로 메모리를 할당하여 삽입할 수 있다.
이로인해 array list는 사용하지 않는 메모리까지도 이미 할당되어있는 상태이기 때문에 노드를 추가 할 때마다 메모리를 할당해주는 linked list가 메모리사용에 있어 더 효율적이다.
-데이터를 중간에 삽입, 삭제하는 경우에도 array list는 다른 data를 모두 이동시켜야 하지만 linked list는 포인터를 이용하여 연결이 가능하기 때문에 더 효율적이다.
linked list 단점 -데이터 접근 속도면에서 봤을 때 array list는 index를 통해 특정 데이터를 바로 가져올 수 있지만 linked list는 특정 데이터를 가져오고 싶을 때 처음 데이터에서부터 next포인터를 통해 특정 데이터까지 접근해야 한다. 이러한 이유로 인해 데이터 접근 속도는 array list보다 느리다.
linked list 구현 코드
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node * next;
};
-data값과 다음을 가리킬 수 있는 포인터로 next포인터의 구성을 가진 노드를 정의해준다.
struct Node * createNode(int value)
{
struct Node * newNode;
newNode = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
-malloc함수는 메모리를 할당해주는 함수이다. 형식은 위의 코드와 같다. malloc 함수를 이용하여 메모리를 할당한 후 입력한 value값을 data에 저장한 노드를 만든다.
void insertNext(struct Node *curr, int value)
{
struct Node * newNode;
newNode = createNode(value);
newNode->next = curr->next;
curr->next = newNode;
}
-노드 삽입을 위한 함수이다. 다음노드에 새로 만든 노드를 연결한다
void insertSort(struct Node *head)
{
struct Node *curr,*p;
p=NULL;
curr=head;
while(curr->next!=NULL){
if(curr->data>curr->next->data){
p=curr->next;
curr->next=curr->next->next;
p->next=head;
head=p;
curr=p;
}
else{
curr=curr->next;
}
}
printf("inserSort result:");
printAll(head);
}
-정렬을 위해 head에 curr포인터를 지정하고 반복문이 실행되면서 curr이 모든 노드를 한번씩 지정하도록 한다. 이 때 curr의 다음 data가 현재 지정하고 있는 값보다 크면 -다음 데이터를 p포인터로 지정하여 노드의 맨 앞으로 빼준다. 뺀 후에는 curr이 다시 맨앞의 노드를 지정하도록 하여 노드를 data 값이 작은 순 부터 정렬해준다.
void *searchNode(struct Node *head, int value)
{
struct Node * curr;
curr = head;
while (curr!= NULL) {
if (curr->data == value)
return curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
-curr이 맨 처음 노드를 지정한 후 반복문으로 모든 노드를 한번씩 지정하게 되면서 value값과 같은 data값을 가진 노드를 지정하게 되면 그 노드를 return해준다.
void delnode(struct Node *head, int value)
{
struct Node *curr, *p;
p=NULL;
curr=head;
while(curr!=NULL){
//삭제할 노드가 첫 노드라면 head의 값을 다음 노드로 지정해준다.
if(head->data==value){
p=head;
head=head->next;
free(p);
printf("'%d'is deleted in this list.\n",value);
break;
}
else if(curr->next->data==value){
p=curr->next;
curr->next=curr->next->next;
free(p);
printf("'%d'is deleted in this list.\n",value);
break;
}
else{
curr=curr->next;
}
}
// value와 같은 값의 data를 가지고 있는 노드가 없을 때 아래와 같이 출력한다.
if(curr=NULL){
printf("!no value that you find in this list!\n");
}
}
-curr이 맨 처음 노드를 지정한 후 반복문으로 모든 노드를 한번씩 지정하게 되면서 삭제 할 노드의 전 노드에 curr이 위치하도록 하고, 포인터 p를 삭제할 노드로 지정해준다.
이는 삭제할 노드의 전 노드와 다음 노드를 이어주기 위함이다.
void printAll(struct Node * head)
{
while(head != NULL) {
printf("[%d]->", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
-head포인터를 이용해 반복문으로 모든 노드를 지정하면서 노드의 data값을 모두 출력하게 한다.
int main()
{
struct Node *head, *temp, *curr;
head = NULL;
curr=NULL;
temp = createNode(3);
head = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = createNode(5);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = createNode(7);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
//새로만든 노드를 temp가 가리키도록 한다. 처음 만든 노드는 head포인터가 가리키게 하고 미리 만들어져 있는 list의 마지막을 curr포인터가
//가리키게 하여 temp가 가리키는 새로 만들진 노드를 curr->next 가 되도록 하여 새로만든 노드와 기존의 list를 연결하여 준다.
temp = searchNode(head, 5);
insertNext(temp, 9);
//temp가 5의 data를 가지고 있는 노드를 가리키게 하여 5다음에 9 data를 가진 노드를 삽입하여 준다.
temp = createNode(2);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = createNode(6);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
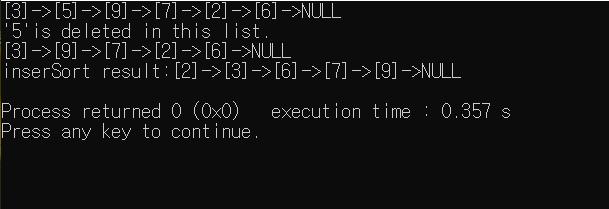
printAll(head);
//만들어진 list를 출력
delnode(head,5);
//5 data를 가진 노드를 삭제한다.
printAll(head);
//만들어진 list를 출력
insertSort(head);
//list를 오름차순으로 정렬한다.
}
###전체코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node * next;
};
struct Node * createNode(int value)
{
struct Node * newNode;
newNode = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertNext(struct Node *curr, int value)
{
struct Node * newNode;
newNode = createNode(value);
newNode->next = curr->next;
curr->next = newNode;
}
void insertSort(struct Node *head)
{
struct Node *curr,*p;
p=NULL;
curr=head;
while(curr->next!=NULL){
if(curr->data>curr->next->data){
p=curr->next;
curr->next=curr->next->next;
p->next=head;
head=p;
curr=p;
}
else{
curr=curr->next;
}
}
printf("inserSort result:");
printAll(head);
}
void *searchNode(struct Node *head, int value){
struct Node * curr;
curr = head;
while (curr!= NULL) {
if (curr->data == value)
return curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void delnode(struct Node *head, int value)
{
struct Node *curr, *p;
p=NULL;
curr=head;
while(curr!=NULL){
if(head->data==value){
p=head;
head=head->next;
free(p);
printf("'%d'is deleted in this list.\n",value);
break;
}
else if(curr->next->data==value){
p=curr->next;
curr->next=curr->next->next;
free(p);
printf("'%d'is deleted in this list.\n",value);
break;
}
else{
curr=curr->next;
}
}
if(curr=NULL){
printf("!no value that you find in this list!\n");
}
}
void printAll(struct Node * head)
{
while(head != NULL) {
printf("[%d]->", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
struct Node *head, *temp, *curr;
head = NULL;
curr=NULL;
temp = createNode(3);
head = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = createNode(5);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = createNode(7);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = searchNode(head, 5);
insertNext(temp, 9);
temp = createNode(2);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
temp = createNode(6);
curr->next = temp;
curr = temp;
printAll(head);
delnode(head,5);
printAll(head);
insertSort(head);
}